Every time we do something on the Internet, we leave traces. We sow a wealth of information about behavior, tastes, habits and so on. The social network accounts, biometric identifiers, usernames and passwords are a real Eldorado for cybercriminals. In the wrong hands, this data can be exploited to harm your employees or your company.
When you consider that :
• 2 out of 3 executives have a personal account open to the public.
• 50% of executives have already seen one of their passwords leaked on the dark web.
• 80% use the same password for 4 to 5 different accounts
(ANOZR WAY data)
It's important to know where the danger comes from, and how to guard against it.
What is a digital footprint?
The digital footprint, or digital shadow, or electronic footprint, represents all the information left behind when browsing the Internet: a like under a publication, a registration on a site, a comment left, a purchase made, etc. It's all the information about a person. A company can also have a digital footprint.
It's made up of a wide variety of information. It can be difficult to be aware of its extent, as it is created either voluntarily or involuntarily, in what is known as the passive or active digital footprint.
Active footprint
What we do consciously. The data we leave behind of our own free will. For example, our full surname on LinkedIn, public photos on our Facebook profile, etc. Social networks alone are a mine of information!
Passive footprint
The kind we don't necessarily realize we have. For example, a phone number in public mode on your Facebook account, because your profile's private mode is incorrectly configured.
Inherited footprint
This is data distributed without our knowledge / leaked data. Such as the online publication of a photo in which we appear, or data published on the darkweb following the hacking of a store, establishment, health center... of which we are customers, patients, etc.
How can an individual's digital footprint impact a company?
Hackers are well aware that the more an attacker knows about his or her target, the more likely the attack is to succeed, as messages can be more personalized. So, to reach a company, hackers are no longer content to look for a software flaw to break into information systems; instead, they are going to target employees. Information gathering by the attacker is a decisive factor in the success or failure of an attack.
For example, he will find out about his target's passions to contextualize his attack. To do this, he'll look at his target's social network profiles, and more specifically at the interests mentioned. If its target likes skiing, he could send a personalized e-mail offering discounts for the next season in Méribel for example.
The digital footprint: an attack surface for employees
The astronomical amount of professional and personal data available on the cyber space is the raw material for malicious individuals to get at you. It can be very risky for a person if it is ignored and not mastered.
There are many ways of collecting data, some more legal than others, and here are just a few of them:
via Internet
Everything you do on the Internet stays on the Internet, but not only that... Every time you surf a search engine, you leave traces behind. For example, your activities on social networks, your browsing behavior, your contacts, your relationships, a profession, tastes, interests, travel habits, sometimes even information about your health. In an unusual example, a user of a web application in the USA unwittingly revealed that she was pregnant, even before her family knews (https://www.forbes.com/sites/kashmirhill/2012/02/16/how-target-figured-out-a-teen-girl-was-pregnant-before-her-father-did/?sh=7d4c683c6668).
The list is unfortunately long and reveals a lot about you. Your Yelp or Google review, when you get back at your insurance company or the restaurant that didn't cook the steak properly, well yes, that review is information.
via third-party cookies and tracking scripts
Third-party cookies are cookies that are set by a website other than the one you're surfing on. They are like little Sherlock Holmes, collecting information about the other sites you visit, keeping track of how long you stay on a page and your personal information when you log in to other accounts. Many of the world's best-known sites are fond of this technology, especially GAFAM.
via data providers & brokers
Who are they? These are infrastructures that store, manage and process an organization's data, and can sell this data for advertising purposes. In France, we have : AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, Scaleway, OVH. In the USA, there are 540 active data brokers.
via your smartphone
This little travel companion, which drives you crazy if you forget it on the table when you leave, is a real spy. That's right, your smartphone records your location data, among other things. Hasn't it ever happened to you that, after shopping in a store, you receive an e-mail from the company in question, asking if you enjoyed the visit? but why? no, it wasn't the store's camera that spotted you (although...) it was your geolocation option that gave you away.
via your phone providers
The major telephone operators track your personal data, and some sell it. Once again, your location is tracked, your web activity, application usage, etc. They know "almost" everything.
The data may seem trivial, but once aggregated and combined, they reveal critical information that can be used to carry out attacks against individuals and their organizations.
How can you become aware of your digital footprint?
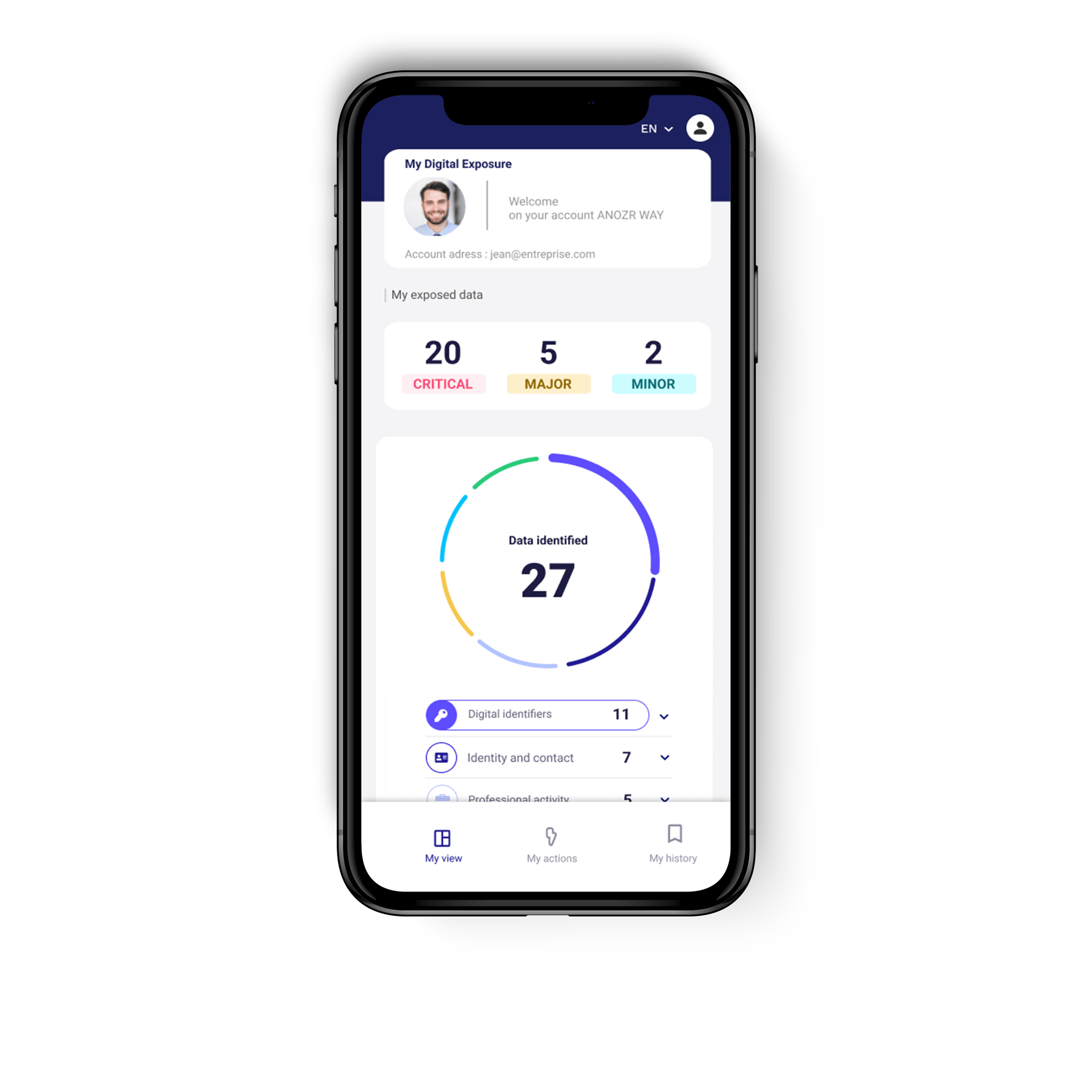
ANOZR WAY can help you control the digital footprint of your employees and executives with its personal protection application. It enables you to detect exposed and compromised data, from social networks to the darkweb: logins, passwords, personal data, professional data, financial data, and so on. And to concretely reduce the digital footprint thanks to corrective actions corresponding to each human vulnerability detected.

You may also be interested in these articles
The Human Factor: the Cornerstone in Cybersecurity
Human vulnerabilities are often the primary entry point for hackers. From ...
NIS2 Directive: Managing the Human Factor
As more than 80% of cyberattacks are caused by human failure, the NIS2 ...
Executives' Physical Security must include the Personal Sphere
Executive Committee members are 12 times more targeted by cyber-attacks ...